First, copper foil can be classified in several ways. Based on thickness, it is categorized into thick copper foil (greater than 70μm), standard thickness copper foil (between 18μm and 70μm), thin copper foil (between 12μm and 18μm), and ultra-thin copper foil (less than 12μm). This classification helps determine the application of the copper foil depending on its mechanical and electrical properties.
In terms of surface condition, copper foil can be divided into single-sided copper foil (single-faced wool), double-sided copper foil (double-sided rough), glossy copper foil (double-sided wool), double-sided copper foil (double light), and low profile copper foil (VLP copper foil). Each type has specific characteristics that make it suitable for different manufacturing processes and end-use applications.
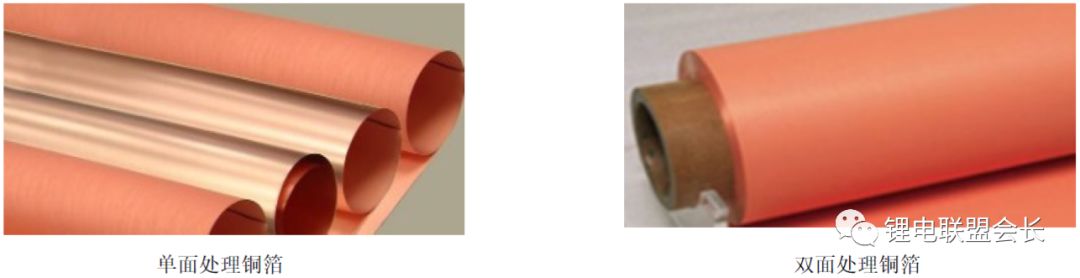
(1) Single-sided copper foil (single-faced wool): Among electrolytic copper foils, this is the most commonly produced type and widely used in the production of copper clad laminates and multi-layer boards. It is known for its versatility and broad application range in the electronics industry.
(2) Double-sided copper foil (double-sided rough): This type is primarily used in fine wiring for multi-layer circuit boards. Its smooth surface ensures high precision after etching, making it a preferred choice for advanced PCB designs. The demand for such copper foil is steadily increasing due to its superior performance.
Copper foil can also be categorized based on its application:
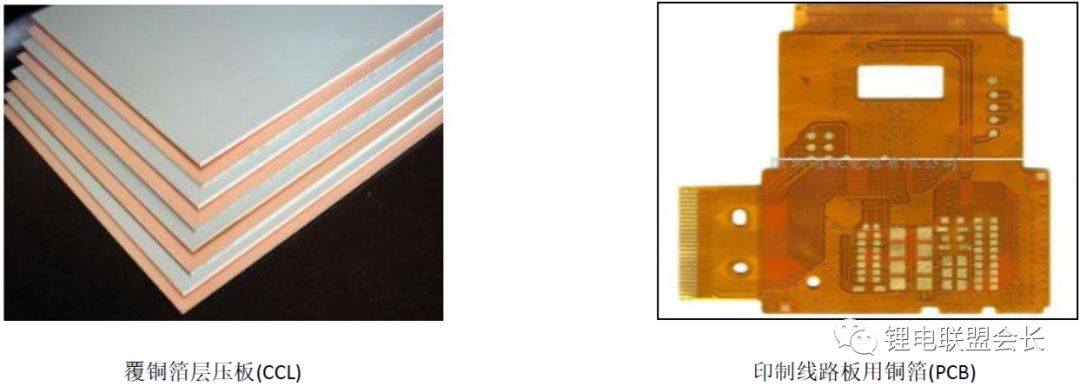
(1) Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) and printed circuit board (PCB) copper foil: These are the most widely used types in the electronics industry. PCBs are essential components in almost all electronic devices, and copper foil plays a critical role in supporting and connecting various components. Most CCL and PCB industries rely on electrolytic copper foil due to its high quality and reliability.
(2) Copper foil for lithium-ion batteries: Copper foil serves as a current collector in these batteries, typically used on the negative electrode side. Due to its good conductivity, soft texture, and cost-effectiveness, it is the preferred material for anode current collectors in modern battery technology.
(3) Copper foil for electromagnetic shielding: Used in medical, communication, and military fields where electromagnetic interference must be controlled. Since rolled copper foil has width limitations, electrolytic copper foil is often used for this purpose due to its flexibility and performance.
Based on production methods, copper foil can be divided into electrolytic copper foil and rolled copper foil. Electrolytic copper foil is produced through electroplating, while rolled copper foil is manufactured by rolling pure copper ingots. Each method offers unique advantages and is suited for different applications.
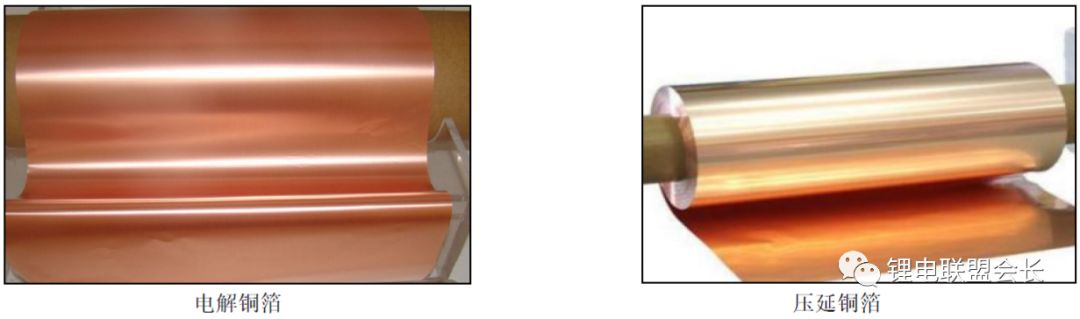
Second, one method for producing copper foil used in lithium-ion batteries is calendered copper foil. It is typically made from copper ingots and goes through several steps, including hot pressing, tempering, scaling, cold rolling, continuous annealing, pickling, calendering, degreasing, and drying. This process requires high-precision equipment and is costly, with imported rolling mills often used for better quality.
Key technology involves controlling the thickness deviation, flatness, and residual stress during the rolling process. Thickness, speed, tension, and surface quality are crucial factors that affect the final product's performance.
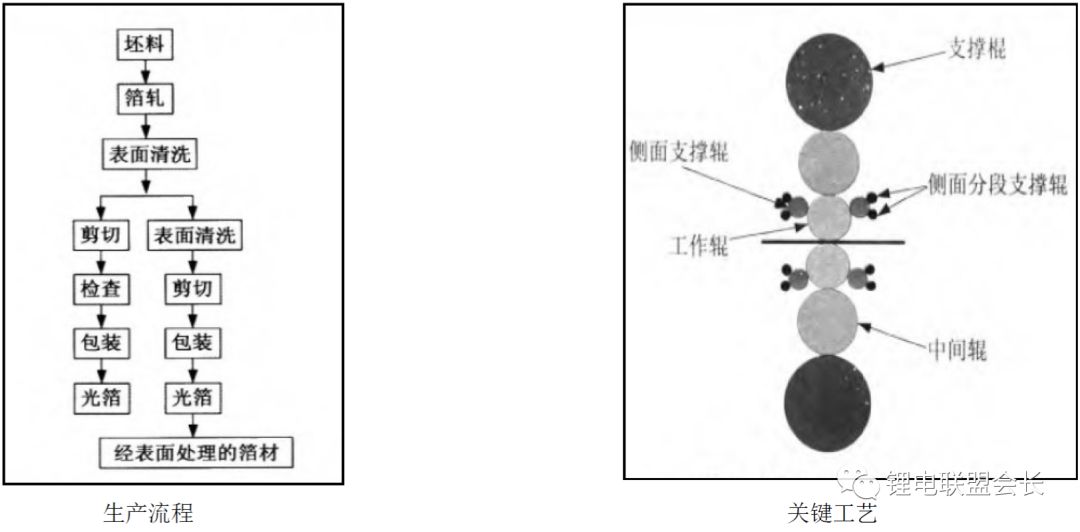
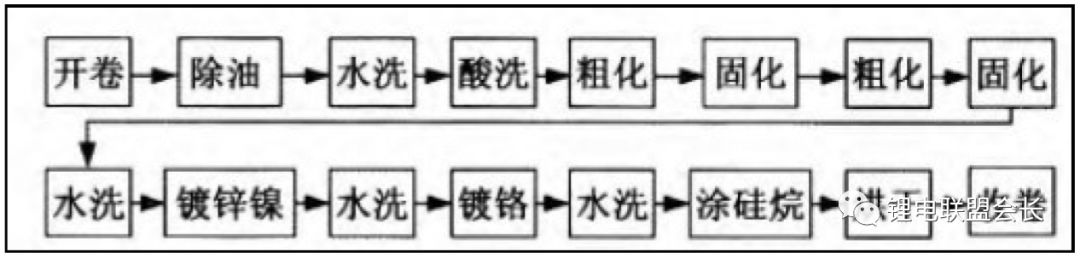
The surface treatment process of calendered copper foil includes cleaning, anti-oxidation treatment, and drying. Cleaning removes oxidation and impurities, while anti-oxidation treatment prevents degradation during storage and use. Drying ensures the removal of moisture without damaging the surface.
(2) Electrolytic copper foil is produced by depositing copper ions onto a rotating stainless steel or titanium cathode roller. The surface closest to the roller is smooth, while the opposite side is matte. This process involves electrochemical reactions, where copper ions are reduced to copper atoms and deposited on the roller surface.
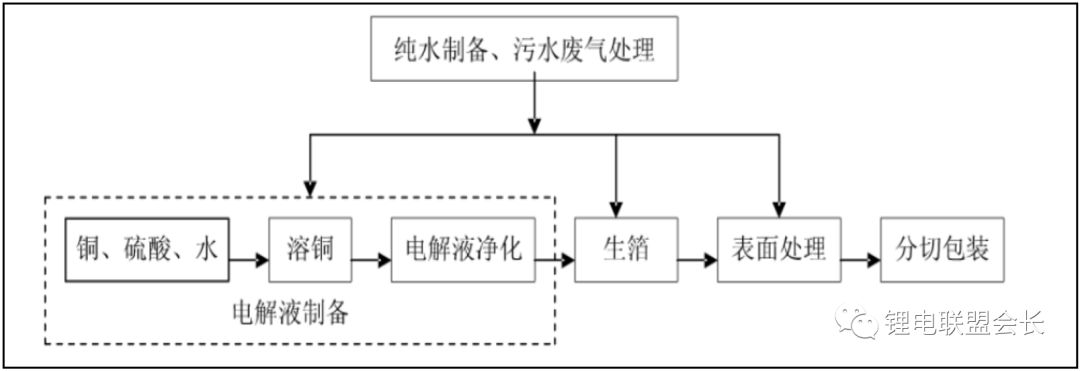
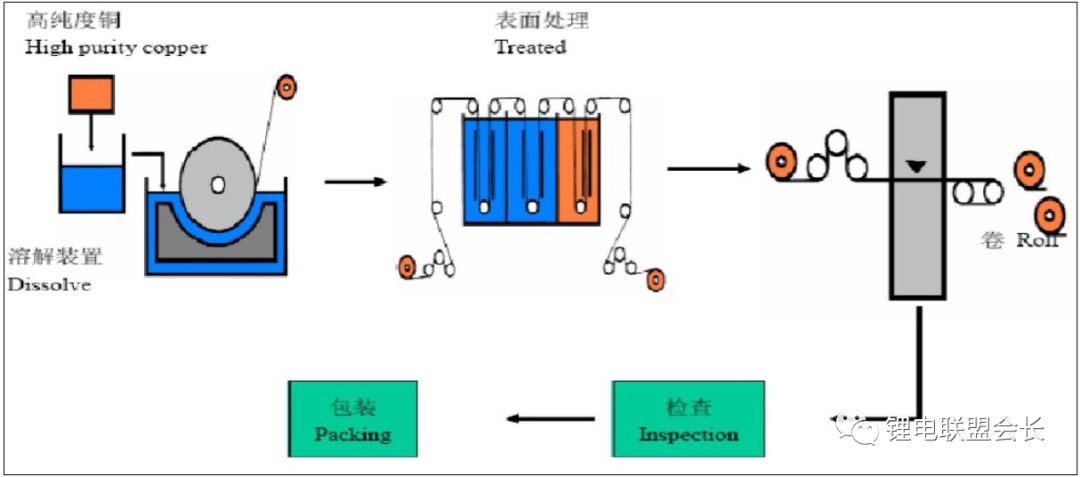
Electrolytic copper foil is widely used in PCBs due to its excellent conductivity and uniformity. It is also preferred in applications requiring high precision and reliability.
The difference between electrolytic and rolled copper foil lies in their production methods, performance, and cost. Electrolytic copper offers better conductivity, while rolled copper provides better flexibility, making it more suitable for bending applications. Rolled copper is generally more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process.
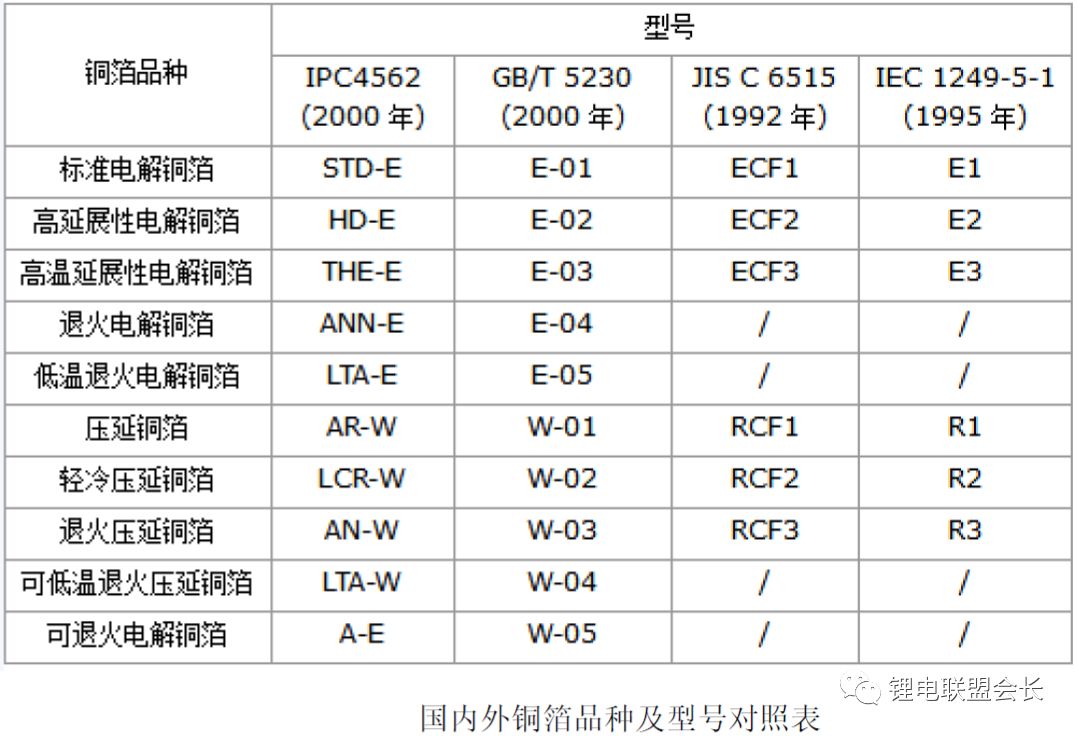
Third, the inspection of copper foil involves checking several key parameters, including thickness, surface appearance, tensile strength, peel strength, high-temperature oxidation resistance, and electrical resistivity. Additional requirements such as elongation, folding resistance, hardness, and surface roughness may also be considered by manufacturers. Each company may have its own testing standards and procedures.
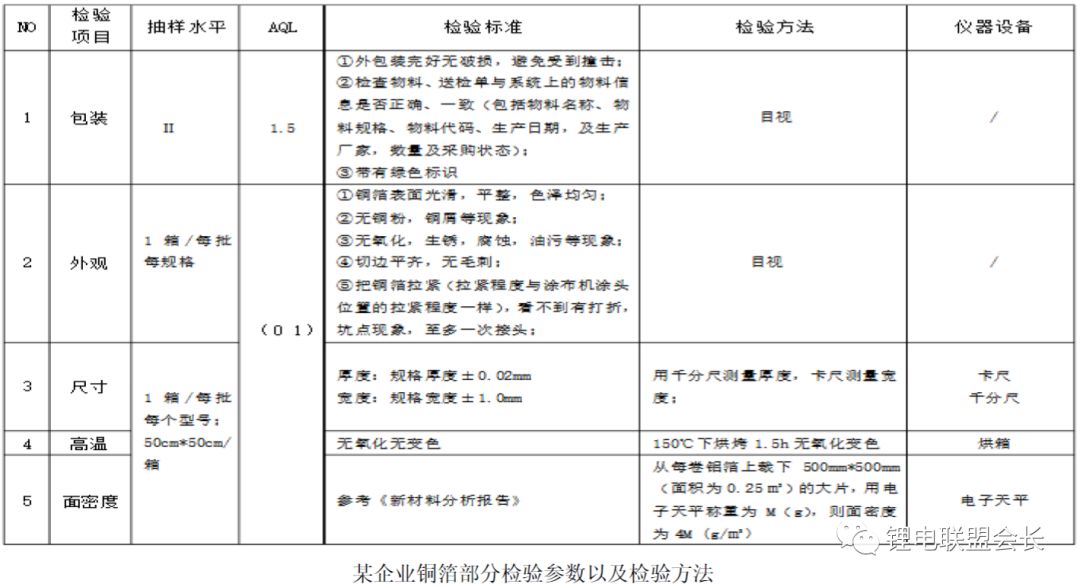
Fourth, the technical development trend of copper foil is moving toward thinner, stronger, and more specialized materials. Ultra-thin copper foil (≤6μm), high-tensile-strength copper foil, porous copper foil, and coated copper foil are being developed to meet the demands of advanced applications like power batteries and high-performance electronics.
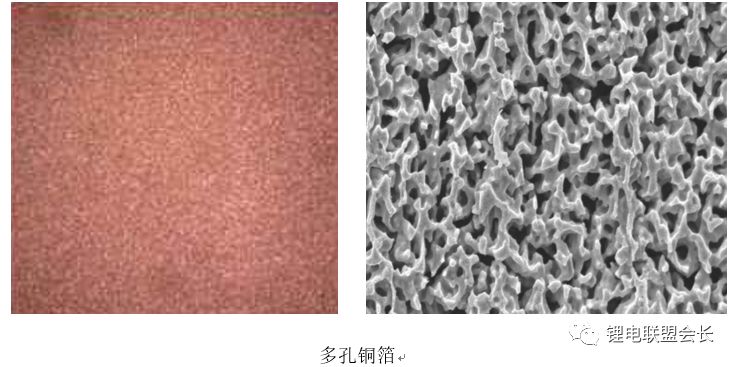
For example, porous copper foil can enhance the performance of lithium-ion batteries by allowing more active material to be loaded and forming a three-dimensional conductive network. However, large-scale production still faces challenges in coating, rolling, cutting, and winding processes.
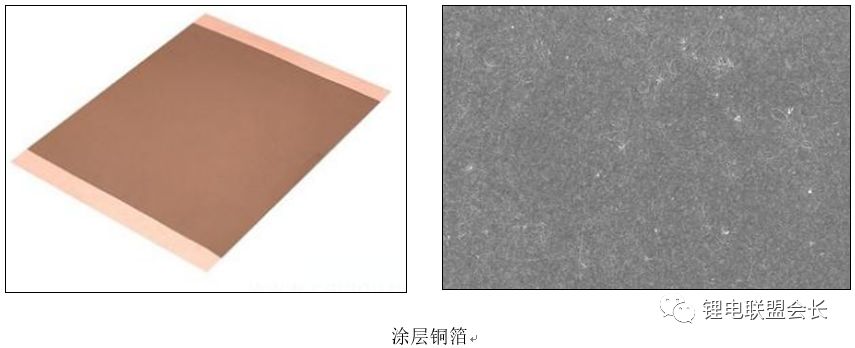
Similarly, coated copper foil can improve adhesion, reduce internal resistance, and enhance electrolyte infiltration. Despite these benefits, it is not yet widely adopted due to compatibility issues with negative electrode materials. Further research and optimization are needed before it becomes mainstream.
Summary: This article discusses the classification, production methods, and future trends of copper foil. The development of any technology relies on repeated experiments, verification, and analysis—tasks that may seem routine but are fundamental to scientific progress. In the new energy industry, continuous efforts from engineers at all levels are essential to drive innovation and achieve sustainable growth.
Dell Certified Refurbished,Refurbished Dell Computers,Used Dell Computers,Used Dell Laptops For Sale
Guangzhou Panda Electronic Technology Co., LTD , https://www.panda-3c.com