**Introduction to NFC**
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables data exchange between devices within a few centimeters. It evolved from contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and was developed by companies like Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors), Nokia, and Sony. Operating at 13.56 MHz, NFC allows for fast and secure data transfer with speeds of 106 kbps, 212 kbps, or 424 kbps. The technology has been standardized under ISO/IEC 18092, ECMA-340, and ETSI TS 102 190, making it widely accepted globally.
NFC combines RFID and interoperability technologies into a single chip, allowing devices to communicate over short distances. It supports both active and passive modes, where one device can initiate communication while the other responds. This makes it ideal for applications such as mobile payments, access control, and ticketing systems. In countries like Japan and South Korea, NFC-enabled phones are commonly used for airport check-ins, building access, transportation cards, and even as digital credit cards.
**Principle of NFC Technology**
NFC is a short-range, high-frequency wireless technology that facilitates non-contact data exchange between electronic devices. It builds on RFID technology and is backward compatible with it. Initially developed by Sony and Philips, NFC is now widely used in smartphones and other handheld devices for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.
One of the key features of NFC is its built-in security. It includes encryption logic circuits in standards like FeliCa and MIFARE, which support secure data exchanges. This makes it particularly suitable for mobile payment solutions. According to the China Internet of Things School-Enterprise Alliance, NFC is often referred to as "safe dialogue" between machines due to its superior security compared to other wireless technologies.
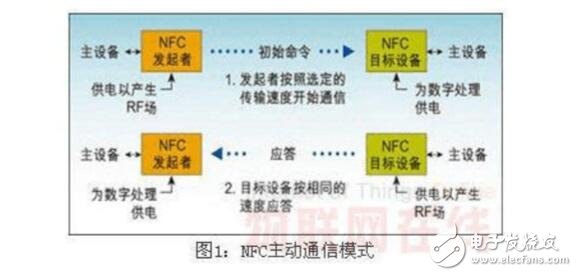
In passive mode, an NFC device acts as a master, generating an RF field to communicate with a target device. The target device uses load modulation to send data back without needing its own RF field. In active mode, both devices generate their own RF fields, enabling faster peer-to-peer communication.
**NFC Technical Characteristics**
Like RFID, NFC uses electromagnetic induction for data transmission, but it offers several advantages. It provides a shorter range, enhancing security and reducing interference. NFC is also compatible with existing contactless smart card technologies, making it a versatile standard supported by many manufacturers.
Compared to Bluetooth and infrared, NFC offers a more secure and convenient way to connect devices. It supports bidirectional communication, which is essential for applications like mobile payments and secure authentication. Unlike RFID, which is typically one-way, NFC allows for mutual authentication and dynamic encryption, including one-time keys (OTPs).
NFC-enabled devices can function as smart cards, readers, or data transfer links. They support various applications, including mobile payments, peer-to-peer communication, and access control. These capabilities make NFC a powerful tool for modern digital interactions.

**Nine Common Applications of NFC Technology**
**1. Financial Payment**
In China, NFC has become a major player in financial transactions. Banks like China Merchants Bank, Everbright, and Guangfa have launched NFC-enabled mobile wallets, integrating UnionPay and TSM (Trusted Service Manager) platforms. While some may think NFC is only for payments, its impact goes beyond that, potentially replacing both cash and credit cards in the future.
**2. Transportation**
NFC is widely used in public transport systems. By tapping an NFC-enabled phone on a reader, users can gain access to buses, trains, and subways. In cities like Shenzhen, NFC-based bus cards are already in use, offering convenience and efficiency. In the UK, London’s bus system now supports NFC payments, paving the way for a future where cards are no longer needed.
**3. Advertising**
NFC tags are transforming the advertising industry by offering interactive and trackable experiences. For example, Microsoft used NFC in a campaign for Halo 4, where players could scan tags to unlock exclusive rewards. This approach encourages engagement and provides valuable data on ad performance, helping advertisers optimize their strategies.
Other applications include smart media, data sharing, access control, and loyalty programs. As NFC continues to evolve, its potential in everyday life will only grow.
Samsung Screen Protector,Tempered Glass Samsung,Mobile Tempered Glass,Tempered Glass Screen Protector Iphone Samsung
Shenzhen TUOLI Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.tlhydrogelprotector.com