**Introduction to NFC**
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that evolved from contactless Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). It was developed by companies such as Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors), Nokia, and Sony, combining RFID with interoperability technologies. NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and has a communication range of up to 10 centimeters. It supports data transfer rates of 106 kbps, 212 kbps, or 424 kbps. The technology has been standardized by international bodies such as ISO/IEC 18092, ECMA-340, and ETSI TS 102 190.
NFC integrates inductive readers, inductive cards, and point-to-point functions into a single chip, enabling secure and fast communication over short distances. Devices can perform identification and data exchange using this technology. While users must have a special mobile phone to use NFC for mobile payments, the technology is already widely adopted in countries like Japan and South Korea, where it is used for airport boarding passes, building access, transportation cards, and credit card replacements.
**Principle of NFC Technology**
NFC, also known as Near Field Communication, is a short-range, high-frequency wireless technology that enables non-contact data transmission between electronic devices within a distance of about 10 centimeters. It evolved from RFID and is backward compatible with it. Initially developed by Sony and Philips, NFC is primarily used for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication in handheld devices like smartphones. Due to its inherent security features, NFC is considered a promising solution for mobile payments. In fact, the China Internet of Things School-Enterprise Alliance refers to NFC as the "safe dialogue" between machines because of its superior security compared to other wireless technologies.
The NFC chip supports mutual communication and includes computing capabilities. Standards like Felica incorporate encryption logic circuits, while MIFARE adds an encryption/decryption module (SAM). NFC is compatible with several standards, including Sony's FeliCaâ„¢, ISO 14443A and B, and Philips' MIFARE. These are commonly referred to as Type A, Type B, and Type F in the industry.
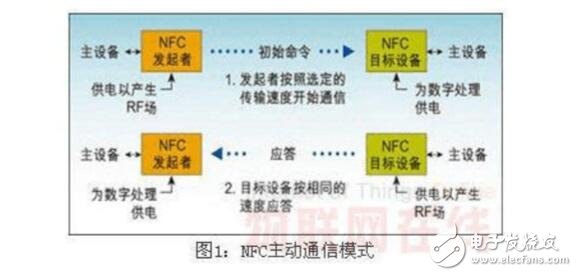
In passive mode, an NFC-enabled device acts as the master, generating an RF field throughout the communication process. It can send data at speeds of 106 kbps, 212 kbps, or 424 kbps. The target device, acting as the slave, uses load modulation to respond without generating its own RF field. This mechanism is compatible with ISO 14443A-based contactless smart cards, allowing NFC devices to detect and connect to them seamlessly.
In active mode, both the initiating and target devices generate their own RF fields for communication. This is ideal for peer-to-peer interactions and allows for faster connection setups.
**Technical Characteristics of NFC**
Like RFID, NFC transmits information through electromagnetic induction. However, there are key differences. NFC offers a shorter transmission range and provides more secure, fast, and easy communication. It is compatible with existing contactless smart card technologies and is now supported by many major vendors. As a close-range communication protocol, NFC enables secure, fast, and automatic device-to-device communication, making it a private and reliable method compared to other wireless connections.
NFC, infrared, and Bluetooth are all non-contact transmission methods, each with unique characteristics suited for different applications. No single technology is inherently better than the others; they serve different purposes.
An NFC-enabled phone contains a built-in NFC chip, allowing bidirectional data transmission, unlike traditional RFID tags that only transmit. This advancement makes NFC ideal for electronic payments, especially since it supports mutual authentication, dynamic encryption, and one-time passwords (OTPs), which RFID cannot achieve. NFC supports various applications, including mobile payments, peer-to-peer communication, and mobile information access.
With NFC phones, users can access entertainment services, make transactions, and retrieve information from any location, at any time, using any device. NFC can function as a contactless smart card, a reader/writer terminal, or a data link between devices. Its main application areas include financial transactions, ticketing, smart media, and data exchange.

**Nine Common Applications of NFC Technology**
**1. Financial Payment**
In China, NFC has become most prominent in financial payment. Banks like China Merchants Bank, China Everbright, and Guangfa have launched mobile wallets integrated with UnionPay and China Mobile’s TSM. This has created the perception that NFC is solely for payments. However, its impact on the financial sector is significant, and in the future, people may rely on NFC and mobile wallets for daily transactions, potentially replacing both cash and credit cards.
**2. Transportation**
Transportation is one of the most basic applications of NFC. By tapping an NFC-enabled device on a gate reader, users can automatically open gates, effectively simulating a transit card. Although some systems like Shenzhen Tong use 2.4G technology, the experience is similar. NFC can also support micro-payments in subway and bus environments. Companies like Shenzhen Jizhi Guoxing and Shenzhen Tong are working on NFC-based bus card solutions.
In the UK, London’s bus system now supports NFC payments on 8,500 buses, allowing passengers to pay with debit, credit, or rechargeable cards. As NFC becomes more widespread, mobile phones could eventually replace physical cards for transportation.
**3. Advertising**
NFC tags have the potential to revolutionize the advertising industry due to their re-readability and ability to track usage. Unlike QR codes, which require precise alignment, NFC is easier to use, especially in dynamic environments like escalators. For example, Microsoft used NFC in a promotional campaign for Halo 4 in Australia, combining NFC tags with QR codes. This approach encouraged users to search for NFC tags to receive exclusive rewards, enhancing engagement and bridging online and offline experiences.
Compared to traditional ads, NFC offers greater interactivity, data collection, and effectiveness, giving it a clear advantage in modern marketing strategies.
Uv Curving Glass
Unveiling UV Curving Glass: A Leap in Screen Safety
The emergence of UV Curving Glass marks a transformative moment in screen protection, particularly for devices with elegantly curved displays.
Advantages of UV Curving Glass for Device Protection
Devices boasting curved displays can now enjoy a tailored protective solution:
Custom Contouring: UV Curving Glass molds to the specific curves of the screen, providing complete coverage that enhances protection.Clarity Maintained: Manufactured from transparent materials, UV Curving Glass allows your device's display to shine through with crystal clear visibility.Resilient Yet Flexible: Combining the toughness of Tempered Glass Screen Protectors with added flexibility, this protector stands up against scratches and minor impacts without obscuring your device's sleek look.Bespoke Screen Shields with Film Cutting Machines
The tailor-made nature of these protectors is made possible through the use of Film Cutting Machines:
Precision Fit: Film Cutting Machines provide exact cuts of UV Curving Glass for a protector that aligns impeccably with your device's unique screen shape.Customization on the Spot: Say goodbye to the limitations of standard screen protectors. With these machines, protectors are custom-sized for any device, ensuring no screen goes unprotected.Completing the Process with UV Curing
The effectiveness of the UV Curving Glass is realized through the UV Curing Protector Screen:
Effortless and Secure Bond: The UV curing step uses light to solidify the adhesive, delivering a snug, bubble-free adherence to the screen.Speedy and Clean: This innovative method completes the curing process swiftly, significantly speeding up the time to final application when compared to traditional adhesive methods.
Why Opt for UV Curving Glass.Choosing UV Curving Glass Screen Protectors presents multiple benefits for the maintenance and aesthetics of your device:
All-Around Defense: The precise fit and strong construction of the protector mean comprehensive protection from daily wear.
Subtle Protection: UV Curving Glass fits so harmoniously with your device that it's virtually indistinguishable, maintaining each device's design elegance.
Pristine Display: The quality of the UV Curving Glass supports a clear and unaltered view of your screen, ensuring a superior visual experience.Designed to Your Device: With the help of a Film Cutting Machine, every Screen Protector is cut to the exact specifications required for your device.
Dive into Advanced Screen Protection with UV Curving Glass
UV Curving Glass is the pinnacle choice for maintaining the integrity of your device's screen. It offers a perfect union of style and security, presenting an unmatched level of fit and protection. Explore the benefits of UV Curving Glass, empowered by the precise capabilities of the Film Cutting Machine and the adhesive activation of the UV Curing Protector Screen, for the ultimate in modern screen protection.
Uv Curving Glass,Tempered Glass Screen Protector,Film Cutting Machine,Uv Curing Protector Screen
Shenzhen TUOLI Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.tlhydrogelprotector.com