This article focuses on the US Department of Defense's MIL-STD-1275, a standard that governs 28V DC power supplies used in military vehicles. Similar national-level standards, such as DEFSTAN 61-5 Part 6 in the UK, also exist to ensure compatibility and reliability under harsh conditions. In aviation, different standards apply—DO-160 for civil aircraft and MIL-STD-704 for military aircraft. While the exact pulse characteristics may vary, the underlying principles remain consistent across these standards.
One of the key challenges in power supply design is protecting against voltage surges, spikes, and ripples. Voltage spikes are short-lived events, typically lasting just tens of microseconds, but they can reach several hundred volts. These are often caused by inductive coupling from lightning strikes or sudden load changes. The current solution involves using transient voltage suppressors, along with EMI filters and power cable inductance, to effectively manage these high-energy events.
Voltage surges, on the other hand, tend to last longer—ranging from tens to hundreds of milliseconds—and can reach up to 100V. They often occur when a load or battery is suddenly disconnected, causing a rapid rise in voltage at the alternator. This can lead to cascading effects, where other connected loads experience the same surge. Addressing this issue is particularly challenging due to its unpredictable nature and potential for repeated occurrences.
Additionally, voltage ripple, which appears as fluctuations on the steady-state power rail, presents another design challenge. Moderate ripple can be filtered out by input capacitors, but with higher amplitude and greater current demands, it becomes more efficient to allow the ripple to pass through the protection circuit to the downstream regulator. This approach helps maintain system efficiency without overloading the protection components.
Traditional passive overvoltage protection circuits (see Figure 1) rely on large, bulky components that introduce insertion loss. This can be problematic in modern systems with increasing power requirements. Furthermore, diverting large amounts of energy to ground doesn't guarantee continued power delivery, and repeated operations may damage the passive components over time.
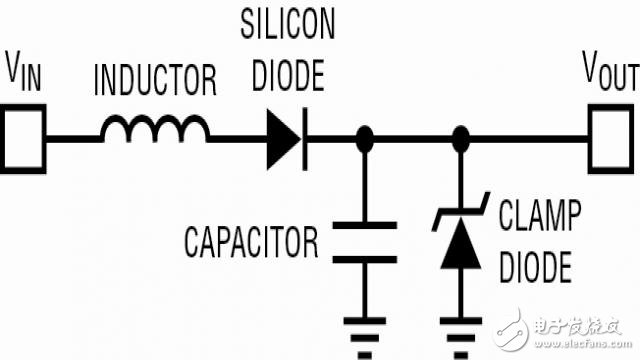
Figure 1: Passive overvoltage protection circuit
A more advanced solution is to use a linear surge suppressor IC, such as the LT4363, which offers improved performance, integrated overcurrent protection, and reduced board space requirements. This type of IC operates similarly to a linear regulator, making it ideal for applications where reliability and efficiency are critical.

Figure 2: LT4363 Surge Suppressor with Current Limit
Under normal operation, an external N-channel MOSFET is fully turned on, acting as a low-resistance path between the input and output. If the output voltage exceeds the set threshold, the MOSFET regulates the output voltage, ensuring continuous power delivery during transient events. This allows the system to remain stable even under unexpected voltage fluctuations.
An optional resistor between the SNS and OUT pins helps manage overcurrent conditions. The current limit loop adjusts the gate voltage of the MOSFET to keep the sense voltage across the resistor at a safe level—typically 50mV. This prevents excessive current from damaging the system.
When either an overvoltage or overcurrent event occurs, a current source charges the capacitor connected to the TMR pin. The charging current is proportional to the input-to-output voltage difference, resulting in a shorter timer period for more severe faults. This ensures the MOSFET remains within its safe operating area, preventing thermal runaway and component failure.
Drop Out Fuse Cutout is a kind of outdoor high voltage protection device, lt is connected with the incoming feeder of thedistribution transformer or distribution lines and primarily used to protect transformers or lines against the impact raised by shortcircuit, overload and switching current. The drop-out fuse cutout is composed of insulator support and a fuse carier, staticcontacts that are fxed on two sides of insulator support and moving contact installed on two ends of fuse carrier, The interior ofthe fuse carrier is the extinguishing tube while the exterior is made of phenolic compound paper tube or epoxy glass.
Composite Fuse Cutout,Cut Out Fuse,Fuse Cutouts Medium Voltage,Dropout Fuse Cutout
Jilin Nengxing Electrical Equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.nengxingelectric.com