Micro-energy frequency converter debugging guide (big circle machine)
I. System introduction Most of the textile industry's large circular machine control system uses the MCU board (or PLC) plus the man-machine interface to control, using the drive to drive.
The circle circular machine trades the control function request of the frequency converter to be relatively succinct, generally adopts the terminal control to start and stop, the analog quantity gives the frequency or uses the multistage speed to give the frequency. The work load of the big circular machine is heavy, and it is required that the jog or low speed operation be rapid. Therefore, the motor drive control performance requires the inverter to control the motor to generate a large low frequency torque. Generally, in large circular machine applications, the inverter operates in a speed sensorless vector control (also called open loop vector) mode to ensure the motor speed accuracy and low frequency large torque output.
During the operation of the circular knitting machine, the reverse rotation and rotation of the motor are absolutely prohibited, otherwise the needle of the needle bed will be bent or even broken. Some circular machines use one-way bearings and may not be considered. If the system is fully reversible depends on the positive and negative control of the motor, you need to set a reasonable parameter, on the one hand to set the prohibition of reverse function, on the other hand need to use DC braking function, using vector control to eliminate the rotation.
Second, micro-energy converter selection for the characteristics of the application of the large circular machine industry, using micro-technology R & D and production of V63 series inverter, large circular machine using the inverter power is basically 3.7KW and 5.5KW, inverter model: WIN -V63-3R7T4,WIN-V63-5R5T4A
III. Scenario 1 Scenario 1 uses analog given frequency
1. Wiring diagram 1) Main circuit wiring diagram

2) Control signal wiring

2. Commissioning steps 1) According to the motor nameplate, set the correct motor parameters to the P3 group of the V63 inverter.
parameter name
Rated power of motor
Motor rated voltage
Rated current of motor
Rated frequency of motor
Motor rated speed
Parameter number
P3.00
P3.01
P3.02
P3.03
P3.04
Setting value
Remove the motor load, press the JOG key to jog operation, and immediately stop the motor after confirming the direction of motor rotation. If the direction is reversed, replace the wiring of any two phases of U, V, and W phases, and set P3.05=2. Press RUN key to auto-tuning the motor parameters. Motor parameters obtained after tuning are automatically stored in P3.06~P3.11.
2), set the parameters
parameter
set up
meaning
parameter
set up
meaning
P0.01
1
Advanced menu mode
P1.00
1
Open loop vector control
P1.01
Not less than the maximum operating frequency of large circular machine, set according to the actual situation
P1.02
Generally set the same as P1.01
P1.04
3
AI1 simulation given frequency
P1.07
1
External terminal operation command channel
P1.11
1
Prohibit reversal
P2.00~P2.08
Set the curve according to the analog frequency needs to be set
P4 group
According to actual effect settings
P6.00
1
Brake first and then start from the starting frequency
P6.01
2
Deceleration stop + DC braking
P6.02
0.20Hz
Start frequency 0.20Hz
P6.04
50%
Start DC braking current is half of the rated current of the inverter
P6.05
0.1S
Start DC braking time 0.1S
P6.09
0.50Hz
Stop DC braking starting frequency
P6.11
120%
DC braking current at shutdown is 1.2 times of the rated current of the inverter
P6.12
2.0S
Set the stop DC braking time reasonably according to the inertia of the system
P6.13
650
Energy consumption braking action voltage
P7.00
1
S curve acceleration and deceleration
P7.03
5.0S
Acceleration time 5 seconds
P7.04
0.8S
Deceleration time 0.8S
Pb.08
0
Terminal control two-wire mode 1
PF.00
0
No stall overvoltage (dynamic braking used)
The big circular machine requires quick response at start-up, low frequency and large torque output, and it should be smooth and soft when stopped to protect the equipment needle bed. Therefore, reasonable setting of the parameters in the above table is the key to giving full play to the performance of the circular machine. The principle is to obtain the best low-frequency torque output capability and reduce the vibration of high-speed circular machine operation by adjusting P4 parameters (low-frequency PI parameters P4.00 and P4.01. Strengthen, high-frequency PI parameters P4.02 and P4.03 weaken, switching frequency P4.04 and P4.05 reasonable settings, adjust P4 group parameters according to the practical effect), by adjusting the start-stop control (P6 group) and acceleration and deceleration time parameters (P7 group) Get the smoothing effect of frequency adjustment.
IV. Scheme 2 Scheme 1 uses multiple frequency given frequencies
1. Wiring diagram 1) Main circuit wiring diagram

2) Control signal wiring
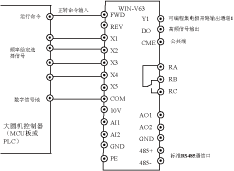
2. Commissioning steps 1) According to the motor nameplate, set the correct motor parameters to the P3 group of the V63 inverter.
parameter name
Rated power of motor
Motor rated voltage
Rated current of motor
Rated frequency of motor
Motor rated speed
Parameter number
P3.00
P3.01
P3.02
P3.03
P3.04
Setting value
Remove the motor load, press the JOG key to jog operation, and immediately stop the motor after confirming the direction of motor rotation. If the direction is reversed, replace the wiring of any two phases of U, V, and W phases, and set P3.05=2. Press RUN key to auto-tuning the motor parameters. Motor parameters obtained after tuning are automatically stored in P3.06~P3.11.
2), set the parameters
parameter
set up
meaning
parameter
set up
meaning
P0.01
1
Advanced menu mode
P1.00
1
Open loop vector control
P1.01
Not less than the maximum operating frequency of large circular machine, set according to the actual situation
P1.02
Generally set the same as P1.01
P1.04
7
Terminal input control multi-speed
P1.07
1
External terminal operation command channel
P1.11
1
Prohibit reversal
P4 group
According to actual effect settings
P6.00
1
Brake first and then start from the starting frequency
P6.01
2
Deceleration stop + DC braking
P6.02
0.20Hz
Start frequency 0.20Hz
P6.04
50%
Start DC braking current is half of the rated current of the inverter
P6.05
0.1S
Start DC braking time 0.1S
P6.09
0.50Hz
Stop DC braking starting frequency
P6.11
120%
DC braking current at shutdown is 1.2 times of the rated current of the inverter
P6.12
2.0S
Set the stop DC braking time reasonably according to the inertia of the system
P6.13
650
Energy consumption braking action voltage
P7.00
1
S curve acceleration and deceleration
P7.03
5.0S
Acceleration time 5 seconds
P7.04
0.8S
Deceleration time 0.8S
Pb.08
0
Terminal control two-wire mode 1
PF.00
0
No stall overvoltage (dynamic braking used)
Pb.00~Pb.03
1/2/3/4
Multi-frequency terminal 1/2/3/4
The big circular machine requires quick response at start-up, low frequency and large torque output, and it should be smooth and soft when stopped to protect the equipment needle bed. Therefore, reasonable setting of the parameters in the above table is the key to giving full play to the performance of the circular machine. The principle is to obtain the best low-frequency torque output capability and reduce the vibration of high-speed circular machine operation by adjusting P4 parameters (low-frequency PI parameters P4.00 and P4.01. Strengthen, high-frequency PI parameters P4.02 and P4.03 weaken, switching frequency P4.04 and P4.05 reasonable settings, adjust P4 group parameters according to the practical effect), by adjusting the start-stop control (P6 group) and acceleration and deceleration time parameters (P7 group) Get the smoothing effect of frequency adjustment.