Analog Analog signal It is a continuously variable signal, such as human voice, music and TV images. Early satellite communication systems were basically analog signals transmitted.
Apogee The point in the elliptical orbit of the satellite farthest from the earth. During launch, a synchronous earth satellite orbiting the earth in a circular orbit is first sent to an apogee of 35,888 kilometers in elliptical orbit, and then ignites a small booster rocket on the satellite. With the help of the rocket's thrust, the satellite enters and merges It has been running on a circular track of 35,888 kilometers.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Asynchronous transfer mode is a method used in broadband digital networks to transmit information between devices in units of cells. Any type of information (such as video, voice, image and other multimedia data) can be carried in the cell carrier and can be operated at high speed. Establish the connection between the source and destination devices through the ATM switch. When the connection is established, any communication between the devices is possible.
AttenuaTIon is the process of reducing the input signal level to avoid overloading the receiver. The attenuator is a passive device, usually placed between the satellite receiver and the coaxial cable. In a differential television system, users who are very close to the differential station often need to use an attenuator to reduce the excessive signal level.
Azimuth (AZ) The angle at which a parabolic antenna of a satellite ground station must turn horizontally when tracking a geostationary satellite. For any ground station, as long as the longitude of the synchronous satellite being tracked is known, the azimuth angle of its antenna should be determined.
BB (Base Band) 6MHz bandwidth signal output from a baseband TV camera, satellite TV receiver or video recorder. Only the monitor can display the baseband signal.
Beta Format Beta system Beta system is a home video mechanism developed by Sony Corporation. This system is incompatible with the VHS system.
Bird A communications satellite typical of communications satellites, weighing about several thousand pounds, with an average life of seven years, it usually "parks" in a circular orbit 35,888 kilometers above the earth. The communication satellite seems to function as an electronic mirror, which forwards telephone, television and data signals sent by various ground communication networks and ground stations, and transmits these signals to the corresponding satellite ground stations.
bit rate The bit rate / code rate of the compressed code stream from the channel to the decoder input.
Blanking In a regular television signal with a frame interval, 25 still pictures or 25 frames of images are transmitted per second. The frame interval time refers to the time interval between the end of one frame image and the appearance of the next frame image. Using this interval, some data signals can be transmitted, but ordinary TV sets cannot receive these data signals.
BNC Connector BNC connector is a standardized small bayonet coaxial cable connector.
C / N (Carrier / Noise) Carrier-to-noise ratio The ratio of satellite signal power to the noise power at the receiving end (expressed in dB). The larger the ratio, the better the TV image quality. When the C / N is lower than 7dB, the quality of the TV image is very bad, and the image quality is excellent when the C / N value is higher than 11dB.
The center frequency of the signal transmitted by a carrier radio or television transmitter. The carrier wave is usually amplitude-modulated or frequency-modulated. In analog satellite TV, the carrier wave is frequency-modulated to transmit image signals and audio.
Carrier Frequency The operating frequency of a radio station, television station, or microwave transmitter. The working frequency of AM broadcast is from 535 to 1600KHz. The working frequency band of FM broadcasting is from 88 to 108MHz. The transmission frequency band of terrestrial television stations is from 54-890MHz. The working frequency band of the microwave and satellite communication system transmitter is from 1 to 14 GHz.
Cassegrain Antenna Cassegrain Antenna (ie, feed-back antenna) is an antenna commonly used in satellite TV reception. The unique secondary reflection structure of the antenna makes it not only eliminates the huge feeder bracket, but also retains the long focal length and high gain. advantage.
CATV Converter cable TV channel preselector cable TV system, a dedicated device connected between the TV and the cable, which replaces the high-frequency head of the TV, allowing users to choose the TV programs of each channel transmitted by the cable at will.
The C-Band C-band frequency ranges from 3.7 to 4.2 GHz, and is used as the frequency band for communication satellite downlink transmission signals.
CDTV (convenTIonal definiTIon television) The term general definition television is used to indicate the analog NTSC television system recommended by ITU-R470.
Channel A frequency band in which a specific signal is transmitted.
Chrominance (chroma) Chroma video signal color information
Circular polarizaTIon uses a circularly polarized antenna to transmit signals to the ground in a spiral form. Some communication satellites transmit two different signals according to the left and right spirals on the same frequency, thus doubling the channel capacity of the satellite.
C Clark Orbit Clark Synchronous Earth Orbit 35,888 km circular orbit, which is operated by a synchronous earth satellite . Although the satellite placed in this orbit rotates around the earth at a speed of thousands of kilometers per hour, the angular velocity of the earth's rotation is the same as that of this satellite. Therefore, from a certain point on the earth, the satellite and the earth are always relatively still.
Coaxial Cable A transmission line that has an insulating dielectric between the center conductor and the outer conductor (or shield). Cable TV uses coaxial cable to transmit TV signals. Home satellite TV receiving antennas and receiver tuner are usually connected by coaxial cable. Compression refers to reducing the number of bits used to represent information.
CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Code) The cyclic redundancy code is added to the bit after the information bit, and is used to check the correctness of the data.
D / C (Down Converter) One of the components of the down-converter satellite TV receiver. Its main function is to down-convert the microwave signal from the satellite into an intermediate frequency signal. At present, the down-converter, low-noise amplifier and feed are integrated into one, so that the intermediate frequency TV signal can be transmitted to the receiver by the coaxial cable of ordinary cable TV.
dBm decibel milliwatt The ratio of signal power expressed in decibels to a reference power source of 1 milliwatt.
DBS (Direct Broadcast Satellite) direct broadcast satellite operating frequency band is above 12GHz. Because the operating frequency of direct broadcast satellites is very high, and the transmission power is also greatly increased, the size of the ground receiver antenna can be greatly reduced for personal direct viewing.
Demodulator A general term for various demodulation circuits used in a demodulator receiver to restore sound or image signals from a carrier signal.
Digital The digital signal has a discrete and variable amount. A typical digital signal has two "states", corresponding to two different signal conditions. Dipole dipole antenna commonly used horn TV antenna is a simple dipole antenna. The feed horn commonly used for satellite TV antennas is also a dipole antenna.
Direc PC A technology for connecting personal computers to Internet services via satellite
Dish-Stretching Technology (or Threshold Extension Technology) Threshold extension technology is used to reduce the noise on the TV screen. There are two commonly used technologies for this purpose. One is the post-reception image processing technology, and the other is the intermediate frequency filtering technology. Because the noise is suppressed, the size of the antenna can be reduced or the signal-to-noise ratio can be improved due to this technology, which is equivalent to reducing the threshold.
Distribution Amplifier is used to amplify TV signals when it is transmitted to the cable network. Shared antenna systems in apartment buildings and hotels also often use distribution amplifiers to increase the load capacity of the antenna system.
Distribution Center TV relay station (or TV relay center) The TV broadcasting station is responsible for transmitting the TV signal from the program delivery agency to the substations and users of the TV network.
The process of dithering energy diffusion in the working frequency band of a satellite transponder with a bandwidth of 36MHz, and a frequency shift of a TV signal with a bandwidth of 6MHz by a triangle wave of 12.5Hz. This process of satellite TV signals actually expands the signal energy to a wider frequency band, which is much larger than the operating bandwidth of the terrestrial TV microwave transmitter, and thus reduces the number of terrestrial microwave machines. interference.
Down Link Down channel communication satellite relays the channel that relays the TV signal to the ground station.
Earth Station The ground station, which receives signals from satellites, is mainly composed of an antenna, a low-noise amplifier, a down-converter, and a receiver. The antenna size of the ground station is usually from 2.4 meters to 27 meters.
EIRP omnidirectional effective radiated power A measure of the power of a satellite TV signal received by a satellite ground station.
EIRP is expressed in dBW (decibels). Usually the EIPR intensity is calculated before the satellite is launched. The calculation result can be drawn as a field strength map of the satellite signal strength changes received at various points in the satellite beam coverage area. There is a direct relationship between the EIRP strength received by the ground station and the required antenna size.
Elevation (EL) Elevation ground station antenna is aimed at the elevation angle of the satellite, measured in degrees. If the antenna is aligned with the horizon, the elevation angle is 0 °, and if the antenna is directly aligned with the satellite above the head, the elevation angle is 90 °.
Entropy coding is a variable-length lossless coding method used to reduce the redundancy of digitally represented signals.
F / D (Focal -Length-to-Diameter ratio) The ratio of the focal length to the diameter of the satellite parabolic reflector to the antenna aperture
FEC (Forward Error Correction) is one of the parameters for receiving digital satellite programs using MPEG-2 technology, usually 1/2, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8, etc.
Feed-horn A component on the receiving antenna of a satellite TV. Its function is to focus the weak signal from the antenna reflection surface and feed it to a low-noise amplifier.
Feed-line is used for the transmission line between the antenna and the receiver. The typical feeder is a coaxial cable.
Field Strength Meter Field strength meter is a measuring instrument used to measure the signal power on the transmission line or antenna.
FM (Frequency Modulation) FM makes the frequency of a sinusoidal carrier wave, according to the modulation process of a certain audio and video signal strength, the modulated carrier wave is transmitted by the antenna, and it becomes an FM broadcast or FM TV signal.
FM Threshold The minimum input signal level required by the demodulator of the FM receiver is called the threshold level. If the input signal is lower than this level, the demodulator cannot recover the complete original signal from the carrier.
Footprint Satellite radiation field strength graph EIRP intensity contour formed by TV satellite beam coverage area. The graph shows the EIRP intensity at various points on the ground. Different transponders on the same satellite have different EIRP field strength maps.
Frequency Reuse frequency reuse uses the geometrical position of the satellite or the polarization of the antenna to separate signals, and to expand the channel capacity in a limited frequency band. In the domestic satellite communication system, a common method of frequency reuse is to make two satellites working in the same band orbit apart by 4 °, because the typical antenna beam width of the 3 ~ 4GHz band is 2 °, so the alignment is "one It is impossible for the ground station antenna of the No. 2 satellite to receive signals from No. 2 satellites that are 4 ° apart, although both satellites are operating in the same frequency band. The second technique is to use the difference between the horizontal and vertical polarization of the antenna to achieve frequency reuse. Therefore, the current satellite is equipped with 24 horizontally polarized and vertically polarized transponders, which can transmit 24 channels of television, but conventional technology can only transmit 12 channels of television.
Frequency-Agile channel selectivity describes the ability of a satellite TV receiver to select 12 or 24 channels from satellites (each transponder works on one channel). If a receiver has no channel selectivity, it means that the receiver only receives a single channel.
Gain The ratio of the output signal of a system to the input signal level, usually measured in decibels (dB).
Geosynchronous synchronous earth orbit is located above the equator in a circular orbit around the earth 35,888 kilometers (22,300 miles) from the earth's surface. GHz Gigahertz (frequency unit), 1GHz = 1000MHz, usually signals with a frequency higher than 1 gigahertz are called microwave signals. High-frequency microwave signals begin to have some characteristics of visible light.
Global Beam Global Beam A form of downlink beam of a global communications satellite. This beam of a satellite can cover one-third of the earth's area. The global beam is composed of three communication satellites respectively located in the Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean. Because the beams of these three satellites cover the entire surface of the earth, any area around several oceans can receive the same signal. Because the global beam coverage area is much larger than domestic satellites covering only one area, the EIRP strength of the global satellite signal is very weak, so the ground station receiving the global satellite signal requires a large antenna, with a typical diameter of more than 9 meters.
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) Greenwich Mean Time International Standard Time (Gorizont (Horizon) horizontal line means that the CIS stationary satellite Gregorian Gregorian antenna is composed of a dual-reflective antenna, the convex hyperboloid is the secondary reflective surface, and the parabolic surface The main reflection surface G / T (Gain / Temperature) quality factor of the terrestrial receiving system. The ratio of the antenna gain of the satellite TV receiving system to the noise of the receiving system is expressed in decibels. If this value increases, it means that the image quality is improved. By reducing the noise temperature of the low-noise amplifier and increasing the size of the receiving antenna, the G / T value can be increased.
Guard Channel frequency guard band to avoid crosstalk between adjacent channels. A few MHz of white space Hertz (Hz) (frequency unit) is left between each adjacent TV channel, which changes every second for one Hertz Huffman coding. It is an entropy coding method. It uses codes of different lengths to represent symbols with different probability of occurrence. Heliax spiral cable is a special coaxial cable with very low transmission loss in the microwave frequency band. It is often used to connect the antenna and the receiver.
ISDB (Integrated-services Digital Broadcasting) integrated service digital broadcasting integrates various signals including still images and moving images, sounds, files, characters and other types of data in a single transmission channel.
The approximate frequency range of the Ka-band Ka band is 30 / 20GHz Kelvin (absolute temperature unit). A temperature measurement unit commonly used in science and technology. K-zero degrees represents absolute zero degrees in physics (equivalent to -273 ° C). The thermal noise characteristic in an amplifier is measured in absolute temperature.
The Ku-Band Ku band frequency band from 11 to 14 GHz is used for satellite communications and direct broadcast satellite TV.
L-band L-band in satellite receivers, its frequency range is about 950 ~ 2150 MHZ Level
LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) ​​A high-sensitivity preamplifier, usually connected to the feed horn of the ground station antenna to reduce the noise temperature of the receiving system and increase its total gain. The most important indicator of a low-noise amplifier is the noise temperature (expressed in absolute temperature K). Generally speaking, the smaller the noise temperature, the better the quality of the TV signal.
LNB (Low Noise Block) high frequency head is a combination of low noise amplifier and down converter, LNB = LNA + LNC LNC (LowNoise Converter) low noise converter (down converter)
LPTV (Low-power TV) A new TV service approved by the Federal Communications Commission in 1980. The low-power TV station has a transmission power of only 100 to 1,000 watts and a beam coverage radius of 16 to 24 kilometers. Scope.
The MATV (Master Antenna Television) shared antenna TV system is commonly used in apartment buildings, hotels, etc. This system can be incorporated into the cable TV system with a little improvement.
MCPC (Multi Channel Per Carrier) In the transmission of satellite digital TV, multiple sets of TV program code streams are mixed by a multiplexer, modulated on a carrier frequency, and then transmitted. After receiving this frequency at the ground receiving station, the demodulated and decoded code stream will be taken out of multiple sets of programs through the splitter, and then processed to watch multiple sets of TV programs.
MDS (Multi-point Distribution System) Multicast TV system is a system that transmits TV signals in a non-directional manner like a radio broadcasting station, but the receiving point is limited and specific.
MMDS (Multi-channel Microwave Distribution System) Multi-channel microwave distribution system uses 2.4-2.6GHz frequency microwave to transmit TV signals, which can be directed or multi-directionally transmitted. MPEG-1 refers to ISO / IEC standards, including 11172-1 (system) 11172-2 (video), 11172-3 (audio), 11172-4 (conformance test) and 11172-5 (technical report).
MPEG-2 refers to ISO / IEC standards, 13818-1 (system), 13818-2 (video), 13818-3 (audio), 13818-4 (consistency).
Offset Antenna The reflective surface of this antenna is only a part of the rotating parabola, usually including poles or vertices, so that when feedforward is used, there is no aperture blocking effect. NT (Noise Temperature) The noise temperature is used to represent the noise of the electronic equipment system or device Characteristic parameters, commonly expressed by K
NTSC (National Television Standards Committee) The National Television Standards Committee of the United States is determined by the committee. NTSC is also the code name for the color television system in the United States. The NTSC standard features 30 frames per second and 525 lines per frame.
PAL (Phase Alternation by Line) A color television coding system designed by Germany for color television. PAL means Phase by Line
Paraboloid Rotating Paraboloid The shape of the classic antenna reflector
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation Coding system) Coding system for pulse code modulation digital transmission
PID (packet Identifier) ​​packet identifier is used in a single program or multi-program transport code stream to accompany a specific integer value of the basic code stream for the decoder to use to identify the nature of the code stream.
Pixel refers to an 8-bit sample of brightness or chroma.
Radio Frequency Spectrum In the electromagnetic spectrum, the frequency range from a few hundred kilohertz to several gigahertz is called the radio frequency spectrum or radio spectrum.
RF Adapter An additional modulator installed between the output of the satellite TV receiving terminal and the input of the user ’s TV. The radio frequency adder modulates the baseband television signal from the satellite television receiver into a radio frequency signal, so that the user's ordinary television can receive these signals on a specific television channel.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) The three main color components of red, green and blue TV
Satellite In space, a small planetary body that orbits a larger planet in a fixed orbit is called a satellite. For example, the moon is the natural satellite of the earth. The artificial earth satellite rotates around the earth around the earth's rotation axis according to its own orbit. Almost all communication satellites are launched into synchronous earth orbit.
Satellite Receiver The satellite receiver works in the microwave band wideband FM receiver. Its main function is to restore the C-band or Ku-band satellite analog TV signals to baseband TV signals.
Satellite Terminal The satellite receiving terminal is a satellite ground station with receiving capability only. It consists of a parabolic antenna, a feeding horn, a low-noise amplifier, a down-converter, and a satellite receiver.
S-Band S-band satellite downlink frequency range is 2.6GHz SCPC (Single-Channel-Per-Carrier) single channel single carrier. It is different from MCPC in that a TV program is modulated separately on a carrier frequency for transmission, and the receiving end is tuned to The program can be received on the corresponding frequency. At present, most of the provincial digital satellite TV is broadcast using SCPC.
Scrambling scrambling code intentionally changes the characteristics of video, audio or coded stream in order to prevent it from being received by unauthorized persons. Of course, this change is processed according to the regulations under the control of the conditional access system, and sometimes it is also necessary to disperse the spectral energy of the signal.
SDTV (standard definition television) The term general definition television is used to indicate a digital television system whose quality is basically equivalent to NTSC. This term is also called ordinary digital television.
SECAM (Sequential Color Memoire) SECAM color system The color TV system adopted by France and the Soviet Union is not compatible with the PAL system. SECAM means sequential color TV memory
S / N (Signal / Noise) The ratio of signal power to noise power, expressed in decibels (dB). S / N is an extremely important performance index in TV.
In the Sparkles noise point satellite TV system, the noise caused by the interference noise on the TV screen, the "noise point" is more obvious than the usual "snow point" of the terrestrial TV system. The only way to eliminate "noise points" is to increase the size of the ground station antenna and use a low-noise amplifier with a lower noise temperature.
Spherical Antenna Spherical Antenna Another major form of satellite ground station antenna. Unlike parabolic antennas, spherical antennas can be aimed at several satellites at the same time, so they have the ability to receive several satellite signals simultaneously. Because of this feature, more and more home satellite TV receivers have begun to install spherical antennas, because these users want to be able to easily switch from one satellite reception to another satellite reception.
Spot Beam is a circular or elliptical cross-section that covers a certain area of ​​the earth's surface. This beam is smaller than the global beam. STV (Subscription Television) Time-paid radio and television. A paid radio and television service.
Sub-carrier Carrier frequency used to transmit audio and other information in a sub-carrier TV signal.
Synchronization technology that keeps the signals of both receiver and transmitter synchronized in time.
Teleconference Many people who are not in the same location use some electronic equipment such as telephone and TV. Meetings held by computer terminals, etc.
Teletext Teletext "Teletext" is transmitted simultaneously with the TV signal and can display text and images on the TV screen. There are usually hundreds of "pages". Each "page" contains 20 lines of Chinese and English characters. "Teletext" is transmitted through the data subcarrier using the frame blanking time in the TV signal. Ordinary TV sets cannot watch "teletext". A special "teletext" decoder is attached to the TV to see "teletext". Now many TV networks and satellite TV systems have added the "electronic newspaper teletext" signal.
Terrestrial TV Terrestrial broadcast TV is a conventional TV that is transmitted in a limited range on the ground. The transmission range is about 160 kilometers in diameter, and the working frequency band is connected to VHF to UHF.
Threshold Extension Threshold extension is a technology that improves the signal-to-noise ratio of satellite receivers by nearly 3 dB.
Translator The function of a translator is to receive a TV signal from a distance, and then convert the TV signal to another channel and then transmit it to the local area to increase TV coverage.
Transponder is composed of a receiver, a transmitter and an antenna, and is an integral part of the satellite entity. The transmission power of a typical communication transponder is 5 to 8.5 watts. (Currently, the transmission power of satellite TV transponders is about tens of watts to one hundred watts.) The C-band operating frequency is 4 to 6 GHz and the bandwidth is 36 MHz. The Ku band is 12 to 14 GHz and the bandwidth is 54 MHz. A group of communication satellites usually has 12 to 24 transponders.
Twin Lead parallel feeder transmission cable commonly used in the 1950s to connect antennas to televisions has now been replaced by better performance coaxial cables.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) UHF band frequency is 300MHz ~ 3GHz. The terrestrial broadcast and television band is 470-890MHz Uplink Uplink channel The channel from the satellite ground station to the satellite to transmit information to the satellite.
Vertical Blanking The process of removing blank lines between frames.
VHF (Very High Frequency) VHF frequency range from 30MHz to 300MHz.
VHS Format VHS format is one of the two most common home video recorder formats. The other is the Beta TV Monitor without a high-frequency TV. It can only receive baseband TV signals and cannot receive VHF and UHF broadcast TV signals. Monitors have higher resolution and image quality than ordinary TV sets.
Waveguide waveguide rectangular or elliptical cross section metal tube is used for microwave signal transmission
Wind Loading Wind pressure is the pressure exerted by the wind on the receiving antenna of the satellite ground station. A well-designed parabolic antenna should be able to withstand a wind pressure load of 64 kilometers per hour, and there will be no obvious damage, and it should even withstand a wind speed of 160 kilometers per hour.
Surface Acoustic Wave Filter (SAWF) The surface acoustic wave filter is made of quartz, lithium niobate, and barium titanate crystals with piezoelectric effect. The so-called piezoelectric effect is the phenomenon that when a crystal is subjected to mechanical action, an electric field proportional to the pressure will be generated. When a crystal with piezoelectric effect is subjected to an electrical signal, it also produces elastic deformation and emits a mechanical wave (acoustic wave), which can convert the electrical signal into an acoustic signal. Since this acoustic wave only propagates on the crystal surface, it is called surface acoustic wave. The abbreviation for SAW filter is SAWF. SAW filter has small size, light weight, reliable performance, and does not require complicated adjustment. The key device to realize adjacent frequency transmission in the cable television system. The characteristics of SAW filters are: (1) The frequency response is flat, the unevenness is only ± 0.3- ± 0.5dB, and the group delay is ± 30- ± 50ns. (2) The SAWF rectangular coefficient is good, and the out-of-band suppression can reach more than 40dB. (3) Although the insertion loss is as high as 25-30dB, the amplifier can be used to compensate the level loss. SAW filters include surface acoustic wave TV image intermediate frequency filters, TV sound filters, and TV channel residual sideband filters. The typical technical specifications of SAW filters are shown in the table below.
Comb filter Comb filter is composed of many pass bands and stop bands arranged at the same frequency interval, allowing only signals of certain frequency range to pass. The characteristic curve of the comb filter is like a comb, so it is called a comb filter. Comb filters have many applications in television technology. The comb filter is used to separate the two orthogonal components of the chrominance signal, the U color difference signal and the V color difference signal. The comb filter is generally composed of a delay, an adder, a subtractor, and a band-pass filter. For still images, comb filtering is performed between frames, that is, three-dimensional comb filtering. For moving images, comb filtering is performed within the frame, that is, two-dimensional comb filtering. Except for occasions with special requirements, most digital TV equipment or high-quality digital TV receivers use a line delay comb filter and a band-pass filter cascade to form a Y and C separation scheme to obtain a satisfactory image quality. The use of comb filters significantly improves the image quality. Solve the interference light spot and interference pattern caused by the bright color string and bright string color; eliminate the color edge creep caused by U and V mixing; eliminate the bright and color fringing.
Attenuator A circuit used to introduce a predetermined attenuation within a specified frequency range. It is generally indicated by the decibel number of the attenuation introduced and the ohm number of its characteristic impedance. Attenuators are widely used in cable television systems to meet the level requirements of multiple ports. Such as the control of the input and output levels of the amplifier, the control of the amount of branch attenuation. There are two types of attenuators: passive attenuator and active attenuator. The active attenuator is combined with other thermal components to form a variable attenuator, which is used in the automatic gain or slope control circuit in the amplifier. Passive attenuators have fixed attenuators and adjustable attenuators. The fixed attenuator is composed of resistors and does not affect the frequency characteristics. It is usually composed of T-type or π-type networks; (for common 75Ω impedance T-type and π-type resistance data with different attenuations, please refer to the book of common antenna TV system); The device is composed of a potentiometer and is used in debugging and level adjustment. It is required that the input and output impedance of the attenuator should match the interface, and the cable system should be 75 ohms. The frequency characteristics of the attenuator must meet the frequency range requirements of the system, and the attenuation of the attenuator in the frequency range should be independent of the frequency. Therefore, commonly used resistance components. Different frequency ranges have different forms of attenuators. Useful coaxial cables are used as attenuators; in waveguide systems, diaphragms that absorb electric field energy are commonly used as attenuators; there are also solid-state diodes (such as PIN diodes) that make waveguides or coaxial systems in the microwave frequency band that can be electrically tuned Attenuator. Attenuators are commonly used in a variety of telecommunications equipment and electronic instruments.
Equalizers are used in telecommunication equipment to correct networks with different attenuation (ie transmission loss) and phase differences caused by different frequencies. Those who can correct the relationship between attenuation and frequency are called "attenuation equalizer"; those who can correct the relationship between phase difference and frequency are called "phase equalizer". Equalizers are often used in cable television systems. The equalizer is usually connected in series in the amplifier circuit, which is set to balance the attenuation of the high-frequency and low-frequency signals caused by the balanced cable transmission. Because the attenuation characteristics of the cable increase with increasing frequency. Commonly used attenuation equalizer is also called amplitude equalizer. It is generally composed of coils, capacitors, resistors and other components. The characteristic impedance of the attenuation equalizer is equal to a fixed value, and its equalization value is the decibel difference of the attenuation between the high and low frequency reference points of the cable. The frequency characteristic of the equalizer is opposite to the frequency characteristic of the cable, but the frequency is low and the attenuation is high, the frequency is high The attenuation is small, using this opposite characteristic to play a balancing role. The equalizer is also often made into a small printed board plug-in structure, divided by the amount of equalization.
The mixer mixes two or more sets of radio frequency programs (signals) with different frequencies to form a broadband RF (signal) multi-channel program output device. In the front-end of the cable TV system, the mixer is the distribution point of the system signal, that is, all the multi-channel RF signals processed by the technology are concentrated at the input end of the mixer, and then the signal output is output to the system network and sent to the user at the mixer output end. . The main technical requirements of the mixer. Operating frequency: If the mixer is broadband, the frequency should meet the requirements of the entire frequency band in the system. If the mixer is a channel type, the frequency should meet the requirements of each channel to be mixed; access loss: When the signal passes through a passive network, it is always hoped that the access loss (insertion loss) is as small as possible. The ratio of the input power to the output power of the mixer is called the access loss of the mixer. Access loss is usually expressed in decibels. When expressed in decibels, it is the difference between the decibel level at the input and the decibel level at the output. Different mixers have different access losses; input and output impedance: In order to match each interface in the entire system, the input and output impedance of the mixer should be 75 ohms; the input terminals are isolated from each other; in ideal In this case, when a signal is added to any input terminal of the mixer, the signal cannot appear at the other input terminals, and when any input terminal has an open circuit or a short circuit phenomenon, the other input terminals should not be affected. But in fact there is always a certain influence. In the case of matching between the terminals, a signal is added to an input terminal, and the difference between the signal level and the signal level appearing at other input terminals is the mutual isolation between the mixer input terminals, generally expressed in decibels . There are different requirements for different mixers, generally requiring greater than 20 decibels.
Intermodulation ratio (IM) When an amplifier in a cable TV system amplifies TV signals from multiple channels, due to the nonlinear effect of the amplifier (mainly the quadratic term), the transmitted signals are mixed with each other, and the resulting sum or difference frequency falls to If you want to enter the TV receiver with the useful signal in the frequency range of the receiving channel, interference will occur, which is called intermodulation for short. Intermodulation is closely related to frequency. Intermodulation interference, which produces moire or twill interference. The intermodulation ratio is defined as IM = 20lg carrier level effective value / intermodulation product effective value. The national standard stipulates that IM≥57dB, and it should be 58dB during design.
Crosstalk modulation ratio (CM) When an amplifier in a cable TV system amplifies TV signals from multiple channels, the image carrier of the desired channel is affected by other (interfering) channels due to the influence of the non-linear devices in the amplifier (mainly the third term) The amplitude of the modulated wave interferes, which is called crosstalk modulation or cross modulation for short. A common phenomenon is that a negative image that interferes with the channel image appears on the background of the image to be received. Sometimes the horizontal synchronization signal of the interfering channel is flipped on the image screen to be received, becoming a vertical white bar, and moving left and right (fixed when the line frequency is consistent), like the wiper of the front window of the car, so also? ". Cross-talk modulation is the modulation of the interference signal transferred to the carrier of the useful signal. Define cross-talk modulation: XM = 20lg peak-to-peak value of transfer modulation on the carrier under test / peak-to-peak and cross-talk to be modulated on the carrier under test The definition of modulation is reversed, and the crosstalk modulation ratio (CM) is defined: CM = 20lg peak-to-peak modulation required on the carrier under test / peak-to-peak value of transfer modulation on the carrier under test CM≥46dB, 48dB should be used in design .
100. Distributor Distributor is the most commonly used component in the distribution network of a cable TV transmission system and is used to distribute signals. Its function is to divide an input signal equally into several outputs, usually there are two distribution, three distribution, four distribution, six distribution and so on. The frequency of the cable TV network continues to increase, and the functions continue to increase, so the requirements for the distributor continue to increase. The main technical requirements of the distributor. Frequency range: The distributor is used in the entire cable TV network, so it should have broadband frequency characteristics; Input and output impedance: The impedance of various RF interfaces in the cable TV network should be 75 ohms to achieve impedance matching, so the distributor input The impedance of both the end and the output should be 75 ohms; Distribution loss: In the system, it is always hoped that the loss of the access distributor is as small as possible. The distribution loss Ls is related to the distribution channel number n. In an ideal case, Ls = 10lgn. When n = 2, the distribution loss of the second distributor is 3dB. In fact, in addition to the loss of the halved signal, part of it is due to the tensile attenuation of the distribution device itself, so it is always larger than the calculated value. For example, the distribution loss of the second distributor is usually 3.5dB, and the loss of the 4 distributor is usually 8dB; mutual isolation: mutual isolation is also called distribution isolation. If a signal is added to one output terminal of the distributor, the difference between the signal level and the signal level of other output terminals is isolated from each other. Generally, the isolation of the output terminal of the distributor is required to be greater than 20dB. In fact, the standing wave ratio is often greater than 1. If the standing wave ratio is too large, the transmitted signal will be reflected at the input or output of the distributor, which will adversely affect the image quality, such as ghosting. Distributors are also divided into over-current distributors, outdoor distributors, indoor distributors, etc. in the project.
101. A sound channel in a mono channel. The process of picking up sound with a microphone and playing sound with a speaker is called mono. In TV broadcasting, the quality of mono soundtrack is not good, especially when it comes to the advantages of literary and artistic programs, especially when it is live broadcast of high-level music performances. In addition, the mono sound can only be broadcast in one language, which is not applicable to a multi-ethnic and multi-dialect country in China. It should be developed as a dual sound (dual channel) to play two languages ​​at the same time, and also create conditions for stereo broadcasting. .
102. Dual sound / stereo The use of dual channels can achieve dual-channel TV sound, and simultaneously play sounds in two different languages, such as standard Mandarin in one way; local ethnic languages ​​or dialects in the other, and the two can be selected at will . You can also use standard Mandarin or ethnic languages ​​all the way; use a foreign language on the other, and you can switch between the two at will. For example, when playing the original foreign TV movie, although Chinese subtitles can be played on the TV screen, it always looks unsmooth, and the double sound can overcome the defects of playing subtitles. Two channels create conditions for stereo broadcasting. Because people's ears can distinguish the distance and direction of each sound source, the listening sound has a sense of space (or three-dimensional). In a sound reproduction system, two or more sound channels are used to make the relative spatial position of the sound source felt by the listener close to the relative spatial position of the actual sound source. This kind of playback sound is called stereo sound. Stereo has two-channel stereo, four-channel stereo, Dolby stereo, Dolby surround sound, Dolby AC-3 digital surround sound and so on. Radio broadcasting using stereo technology is called stereo broadcasting. Take two-channel stereo broadcasting as an example. Two-channel stereo broadcasting is to broadcast two sound signals corresponding to two directions of the listener's front left and front right through one or two broadcast channels with different frequencies. The listener uses a stereo radio with a two-channel playback system to receive, and can identify the relative position of the sound source to produce a sense of stereo; the same program content can also be received with an ordinary radio, but there is no stereo sense. In order to meet monophonic compatibility, FM stereo broadcasting with a pilot system is mostly used. It uses only one FM broadcast channel, using the modulated basic sound frequency? "Left plus right" signal, subcarrier AM band and pilot to send "left minus right" signal. In theory, in order to obtain the best stereo effect, the ideal method An infinite number of microphones are used to pick up the sound signal, and then an infinite number of sound channels are used to transmit the sound to an infinite number of speakers and replay. As long as the position of the speaker corresponds to the position of the microphone, the reproduced sound can accurately reproduce the scene The sound of the audience gives the audience a three-dimensional sense of the immersive scene.
103. Surround sound surround sound refers to the playback mode in which direct sound and reflected sound surround the listener. Therefore, the more speakers, the stronger the sense of being surrounded by the listener. Two-channel stereo can only discern the relative position of sound sources. The four-channel stereo system uses four microphones and four speakers. Two of the four microphones are close to the stage, picking up the direct signal of the stage, and the other two are farther from the stage, picking up reverberation signals that reflect the effects of ambient sound. The signals picked up by the four microphones are transmitted to the four speakers by four independent sound channels. Corresponding to the position of the microphone, the speakers are front left, front right, rear left, and rear right; where the front left and front right are used to replay the direct sound of the stage, and the rear left and rear right are used to replay the mixture reflecting the environmental effects. sound. The listener has speakers in front and rear, which not only has a sense of presence in the horizontal direction, but also feels surrounded by sound, so it is also called surround sound.
106. Dolby AC-3 digital surround sound AC-3 technology originated from providing high-quality sound for high definition (HDTV). AC-3 technology is developed from Dolby AC-1 and Dolby AC-2. AC-1 reduces the number of channels by half in a 4-2-4 multi-channel matrix (so that the transmission capacity can be reduced), and then uses incremental modulation (delta modulation) technology for digital encoding. Therefore, the compression factor of AC-1 is twice. With the advancement of sound coding technology and digital signal processor (DSP), the AC-1 system has developed into an AC-2 system based on transform coding technology. While improving quality, the compression factor has further changed to 4 times, but multi-channel Matrix processing technology remains. AC-3 is developed on the basis of AC-1 and AC-2. It inherits many advantages of AC-2, such as window processing, transform coding, adaptive bit allocation, etc., but also overcomes their deficiencies And limitations. AC-3 has 5.1 channels, that is, left, center, right, left surround, right surround and 0.1 low-effect sound channels. The left and right surround channels here are independent channels made separately, which are more lively and realistic. . Based on Dolby AC-3 technology, there are currently 6.1-channel and 7.1-channel digital sound return systems. AC-3 is the sound system of HDTV in the United States. This system has been recognized worldwide. Note: 4-2-4 represents four-channel recording when recording. When the recording is placed on film, the 4 channels are compressed to two channels by encoding technology. When the sound is restored, 4 sounds are still reproduced. Original sound.
107. Panda Sound (PANDA-1) In the early 1980s, the American Wegener Communications Company designed a set of practical TV sound high-fidelity multi-channel multi-language sound demodulation circuit technology, which was named "PANDA-1" (Chinese Translated "Panda-1" high-fidelity multilingual stereo sound), and has obtained a technical patent in the United States. This sound technology is an analog noise suppression system. Its function is to transfer a normal sound, generally with a high frequency bandwidth of 280KHz, and it uses half the high frequency bandwidth of 130KHz to transmit the baseband audio signal with a bandwidth of 15KHz. The dynamic range of the audio signal is compressed at a specific ratio of tens of times to a very narrow bandwidth. In this way, each set of image programs can simultaneously provide up to six audio channels for stereo or bilingual broadcasting, and can simultaneously transmit independent radio programs, that is, three sets of stereo or six mono channels can be transmitted on different frequencies Road. PANDA-1 sound is used in analog channels and is also analog compressed, so the sound quality is quite different from the digital sound signals currently used, but because of the bandwidth savings, there are several more channels. To receive PANDA-1 sound, the receiver needs to have an expansion circuit audio carrier demodulator, otherwise the received sound is high noise and high distortion sound. Any receiver with PANDA-1 demodulation function can choose to listen to six accompanying sounds or two-channel stereo sound at will, through remote control operation, screen display, and audio programming reception.
108. NICAM (NICAM) NICAM is a quasi-instantaneous companding sound multiplexing, which is a digital sound processing technology. Its main features are high signal-to-noise ratio, wide dynamic range, and sound quality comparable to CD. Therefore, NICAM is also called NIAM. For Liyin, Liyin is a common name for the digitalization of radio and television sounds. In China's terrestrial broadcasting and satellite broadcasting, the frequency of TV sound is FM. Liyin adds a digital sound sub-carrier frequency on the basis of the original sound sub-carrier frequency. The sounds form a dual-carrier mode and do not interfere with the original mono signal. Using AM-FM, FM-FM playback mode. The Liyin mode has a stereo mode, that is, left and right channels; a dual voice mode, that is, two voices are transmitted from the left and right channels at the same time, or two mono broadcasts, or one mono broadcast and one data. When transmitting, it is processed with a special modulator and then transmitted together with the TV image signal and analog audio signal. When receiving, you can listen to the digital stereo sound program comparable to CD after processing with a dedicated Liyin demodulator. There are more than 0 types of Li-Gang in the world. China adopts NICAM and D Liyin system. On the basis of retaining the original analog FM audio secondary carrier frequency, a second secondary carrier frequency of 7.28MHz is added, and quasi-instantaneous companding coding technology is adopted. At present, in the first and second sets of satellite transmission systems of China Central Television, three sets of Central People's Broadcasting Station programs of Central One, Central Two, and Central Three are inserted using NICAM-728. When receiving satellite digital sound broadcasting signals, the satellite receiver needs to have a baseband output, connect it to the NICAM-728 receiver, and receive stereo signals after processing it, so that you can easily obtain high-quality CCTV broadcasting program signals source. The transmission of Liyin signals in the broadcasting of terrestrial TV stations marks the beginning of the era of digital stereo sound in TV sound. At present, some TV sets have the NICAM receiving function, but they need to be in the same format to receive Liyin. Otherwise, they cannot listen, and it is necessary to distinguish whether they meet the Chinese Liyin standard.
113. Solar cell Solar cell is abbreviated as solar cell. It is a device that directly converts solar energy into electrical energy using the photoelectric effect of semiconductor silicon. Solar energy has 1.4kw / m2 per 1m2 in the earth's cosmic space. On sunny days, it has 1kw / m2 per 1m2 on the ground. Most of the solar cells used on satellites are silicon single crystals. Solar energy is converted into electrical energy. Theoretically, the photoelectric conversion efficiency can reach 25%, in fact not more than 16%, generally about 10% -13%. In recent years, a gallium arsenide single crystal element with high conversion efficiency, high-temperature operating characteristics and excellent radiation resistance characteristics has been frequently used. The solar cells in use today have many small silicon solar cells connected in series and parallel to form an array. The size of a solar cell is 2 × 2cm2, 2 × 4cm2 and 4 × 4cm2. Its thickness is 0.15 ~ 0.4mm. The number of cells in series in a solar cell array depends on the requirements of the output voltage, and the number of parallel connections depends on the requirements of the output current. The total number of the two combined determines its output power. For example, Japan ’s Broadcast Satellite (BS-2) uses about 11,000 silicon solar cells. The power obtained by solar cells is not all used directly, but a part of it is stored in the storage battery in the satellite. When the satellite is in the shadow area on the earth and the solar battery does not generate electricity, the storage battery supplies power to all parts of the equipment to work. Silicon solar cells are currently the main force in space batteries, accounting for about 80%, and will also occupy a major position in future applications, so it is very important to improve the efficiency of silicon solar cells. The use of gallium arsenide solar cells is also gradually increasing, these two solar cells will be the main force of space energy.
114. Quick star-changing skills for a long time, the free dinner of ETTV in Asia 2 (100.5 ° E) has become a hot spot for most TV enthusiasts. Some people said that they would encrypt during the Spring Festival, and it was not until 10 July It stopped broadcasting, leaving only 4 programs in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, and Shanxi. All the TV fever friends were busy changing stars. Pulling the power cord, moving the receiver, and the monitor are all necessary. Compared with the initial installation, only a few holes are drilled. Who is willing to run up and down the balcony on the roof of the sun? Regardless of your skills, proficiency also makes you tired and sweaty. If it is okay to equip with one set, there are a lot of friends waiting for you! Therefore, I will introduce the technique of rapid star adjustment to everyone and let the majority of satellite TV enthusiasts enjoy it together. Now I will replace the Asian 2-100.5 ° E satellite with the Asian 2R 76.5 ° E satellite as a demonstration. Take Wenzhou, Zhejiang as an example: city latitude 28, east longitude 120.7, Asia No. 2 azimuth A38 elevation E50.46, Asia Pacific 2R. Azimuth A64.18 Elevation E31.94. (Refer to "TV Weekly 1999 Star Hunting Manual") The basic operation steps are as follows: 1. Turn on the TV and satellite receiver, and receive Beijing TV station normally. (If it means that there is a fault in some part of the system, you must check it again.) ①Press Press the key to pop up the main menu, press the △ key to move the cursor to program addition or antenna adjustment, (depending on the model) If the same machine can press the button to directly display the program search menu. ② After entering the program adding menu, the downlink frequency is changed from the original 12329 to the 12530 symbol rate from the original 06930 to the 30,000 polarization and the original vertical to the horizontal. (It depends on your installation of the high-frequency head.) Now leave one person to observe in the room At this point, you can go up the roof. 2. Bring a 10-12 torx wrench, 1 ordinary protractor (1 yuan for a stationery store, a small hole in the middle, a thread can be used to tie a knot, and a nut on the other end). can. 3. Calculate the number of elevation angles first, 50.46-Asian 2R 31.94 = 18.52 in Wenzhou, Asia 2, because there are different manufacturers of antennas, the accuracy is also different, no matter how much the antenna is deviated, you first move the protractor to the high frequency head support It depends on how many degrees it reads immediately (see Figure 1). The elevation angle of Asia 2 is 50.46, now you can add 18.52 according to the actual measured degree. For example, 50.46 + 18.52 = 68.98, then loosen the two left and right elevation adjustment screws until they are locked at 68.98 degrees (see Figure 2), and then loosen the azimuth fixing screw to turn more than 20 degrees westward, and use the mobile phone to connect the indoor phone , And then slowly turn westward a bit, and the signal will appear immediately when the QPSK Eb / No reaches the maximum, and then lock. (For example, the brightness of the mobile phone display can be used at night to help read the protractor degree without borrowing lights). It took me only 2 minutes and 50 seconds to change the star at the fastest time. After finishing the above work, I can enter other frequencies indoors. (For example, 12278 V 22425, 12308 V 224525, 12650 V 30000, 12405 V 30000, 12629 H 30000, 12374 V 05660) Of course, it is not a problem, if you use this method to calculate other satellites, it is also very convenient.

Follow WeChat

Download Audiophile APP

Follow the audiophile class
related suggestion
TV LAN broadcasting technology is relatively mature, because of various restrictions such as local LAN gateways and firewalls, making WAN satellite TV live broadcast difficult ...
LAPIS Semiconductor, a subsidiary of ROHM, has developed 4 inputs and 4 outputs for satellite TV receiving antennas ...

Strategy Analytics Service Provider Strategy (SPS) service released the latest research report "Global Digital TV Forecast" ...
NXP's CX24109 is a highly integrated direct down conversion digital satellite TV tuner, suitable for digital video, audio and data receivers ...
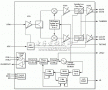
As the window of satellite TV, the satellite antenna system occupies a very important position in the cable TV system. The advantages and disadvantages of the satellite antenna and the focus of its feed ...
Encyclopedia of Projector Lumens ANSI Lumens is a special unit determined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology to measure the luminous flux. ...
Encyclopedia of commonly used terms for connectors 1. Connector: It is usually attached to a cable or a device, and is a separable element for the electrical connection of a transmission line system.
Comprehensive wiring terminology (table) English name
The lift of water pump is used to overcome altitude and resistance, high lift mean that, in water cooling computer system, water pump overcome the pipe resistance power is stronger. It can apply to all kinds of the complex water channel pipe, promote heat dissipation wonderfully. The lift is the main standard to measure the performance of a pump. Lift refers to the maximum height the pump can push water to when the flow is zero.
The water pump with high lift, it is suitable for complex waterway. If it has a lot of the Water Block in the waterway , recommand use the high lift water pump.
Great Lift 12V Dc Water Pump,Silent Cool Water Pump,High Lift Cooling Pump,Luquid Cooling Pump
Dongyuan Syscooling Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.syscooling.com