Did you know that the input signal can significantly influence your choice of the best successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for your application?
When we think about "input," we often consider factors like frequency, amplitude, sine waves, or even sawtooth signals. These are all important when optimizing signal conditioning. However, one aspect that many engineers overlook is the actual type of input used in a SAR ADC. In this post, I'll explore three common types of SAR ADC inputs: single-ended, pseudo-differential, and fully differential, and how they can be applied in real-world designs.
In future posts, I’ll dive deeper into the performance differences between these input types and share practical tips to help you achieve optimal ADC performance. For now, let’s take a closer look at each input type and understand their characteristics and applications.
Single-Ended Input SAR ADC
Single-ended inputs are the simplest form of SAR ADC input, as they only have one input pin. The ADC converts the signal relative to its internal ground, provided the input signal stays within the specified range. This configuration is commonly used in applications where the signal is unipolar, such as power supply monitoring.
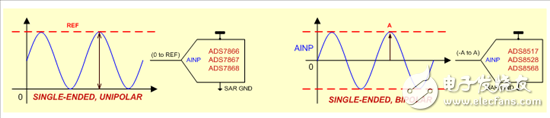
Figure 1: Single-ended conversion example
Some single-ended SAR ADCs can also handle bipolar signals, where the voltage swing may exceed the supply rails. These devices are often used in systems with multiple channels or in applications requiring simple signal acquisition.
Pseudo-Differential Input SAR ADC
A pseudo-differential SAR ADC has two input pins, but only one of them changes dynamically while the other is held at a fixed reference voltage, typically REF/2. The difference between the two inputs (AINP - AINM) is then converted into a digital code. This configuration offers better noise rejection compared to single-ended inputs and is commonly used in shunt current sensing applications.
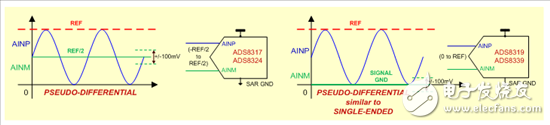
Figure 2: Pseudo Differential Input Configuration
In some cases, the fixed input (AINM) can be connected to ground, making it function similarly to a single-ended input. This flexibility allows designers to choose the best configuration based on their system requirements.
Fully Differential Input SAR ADC
Fully differential SAR ADCs use two complementary input signals, where the difference between the two (VDIFF = AINP - AINM) is converted. These ADCs are ideal for high-performance applications due to their superior noise immunity and dynamic range.
Most fully differential SAR ADCs have a defined common-mode voltage range (VCM = (AINP + AINM)/2), usually centered around REF/2. However, newer designs offer extended common-mode ranges, allowing for more flexible signal handling.
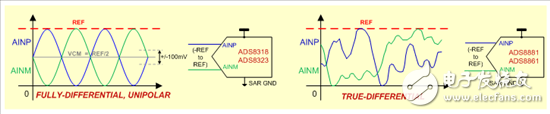
Figure 3: Fully Differential Input Configuration
Fully differential ADCs are widely used in transformer-based systems and high-precision measurement setups. They support both bipolar and multi-channel configurations, making them versatile for a wide range of applications.
PZT Piezoelectric Cylinders/Tubes
Yuhai company develop and produce of various tube/cylinder sizes, bearing variety of electrode and metallisation configurations. The tubes is fabricated from various published and additional custom in-house Piezoelectric Material formulations for applications such as high power, sensitivity, stability needs.
Features
- · Choice of metallisation (Silver, Nickel, Gold and others on request)
- · Evaporated and chemically deposited metallisation's available
- · Thickness/Radial frequency tuning available on request
- · Wrap around electrode configuration
- · Wide choice of PZT formulations
aApplications include
- · Hydrophones
- · Fibre optic stretcher
- · Augmented reality
- · Torpedo decoys
- · Accelerometers
- · Pressure sensors
- · Print head transducers
- · Oil and gas exploration
- · Scientific equipment
Tubes
Height:
1-100mm
OD:
6-180mm
ID:
5-150mm
Wall: 0.5-15mm
Piezo Tube,Piezoelectric Tube,Piezo Electric Tube,Piezo Ceramic Tubes
Zibo Yuhai Electronic Ceramic Co., Ltd. , https://www.yhpiezo.com