1. Continuously improve the projection of semiconductors

At the heart of every DLP® projection system is an optical semiconductor called the DLP® chip, which was invented in 1987 by Dr. Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments.
The DLP chip is probably the most sophisticated optical switch in the world. It contains a matrix of up to 2 million micromirrors mounted on hinges; each micromirror is less than one-fifth the size of a human hair.
When the DLP chip is coordinated with a digital video or graphics signal, the source micromirror and projection lens can reflect the digital image onto a screen or other surface. The DLP chip combines advanced electronics around it to produce stunning images and video that redefine picture quality.
2. Grayscale image
The micromirror of the DLP chip can be tilted (turned on) or away from the light source (off) in the DLP projection system. This can cause pixels to be either bright or dark on the projection surface.

The bitstream image code of the input semiconductor directs each micromirror to switch thousands of times per second. When the number of times the micromirror is turned on more than the number of times off, the light gray pixels will be reflected, and the dark gray pixels will be reflected when the number of times the micromirror is turned off more than the number of times of opening.
In this way, the micromirrors in the DLP projection system can reflect up to 1024 grayscale gradient pixels, converting video or graphics signals entering the DLP chip into very detailed grayscale images.
3. Add color
The white light generated by the lamps in the DLP projection system passes through the color filter as it propagates to the surface of the DLP chip. This feature filters at least red, green, and blue light, and a single-chip DLP projection system produces at least 16.7 million colors.
BrilliantColorTM technology adds new colors (including cyan, magenta, and yellow) to enrich the color palette for richer color performance. Some DLP projectors offer solid state lighting that replaces traditional white light. Therefore, the light source can emit the necessary colors to avoid using the color filter. The 3-chip architecture in some DLP systems is ideal for high-brightness projectors required for large venue applications such as concerts and cinemas. These systems are capable of producing over 35 mega colors.
The switching state of each micromirror is coordinated with these basic color building blocks. For example, a micromirror that is responsible for projecting purple pixels will only reflect red and blue light onto the projection surface; these colors will then be mixed to see the expected color in the projected image.
4. Application and configuration
Single chip DLP projection system
Many data projectors and HDTVs that use DLP technology rely on a single-chip configuration as described above.
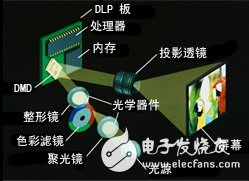
White light passes through the color filter, causing the surface of the DLP chip to appear red, green, and blue, or even other primary colors (such as yellow, cyan, magenta, etc.). The ratio of the switches of the lenses to the time they are "on" or "off" is coordinated according to the color they illuminate. The sequential colors will then blend to produce the full-color image you see on the screen.
3 chip DLP projection system
Projectors using DLP technology and large-scale stadium projectors for ultra-high-brightness applications (such as movies) rely on a 3-chip configuration to produce stunning images, whether static or dynamic.

In a 3-chip system, the white light generated by the lamp is split into red, green, and blue by the prism. Each DLP chip is dedicated to identifying one of these three colors; the colored light reflected by the micromirrors will then be combined and passed through the projection lens to form an image.
Regardless of the application or design, projectors using DLP technology continue to improve the standard of picture quality and video performance. Its starting point is a small imaging chip consisting of millions of micromirrors called DLP that produce stunning images.
Yuhai company develop and produce of various rings sizes, bearing variety of electrode and metallisation configurations. This variety of Rings is fabricated from various material formulations for applications such as high power, sensitivity, stability.
Features
· • electrode type on request
· • Surface roughness on request, for specific demanding application
· • Thickness/Radial frequency tuning available on request
• Wide choice of PZT formulations
Applications include
• Sensors
• Welding
• Ultrasonic cleaning
• Precise Measurement
• Ultrasonic scalpel
• Cauterisation
• Phacoemulsification
• Therapeutic ultrasound
• Accelerometers
Dimension range
|
Outer diameter |
3-180mm |
|
Inner diameter |
1-150mm |
|
Thickness |
0.2-25mm |
Piezo Ring,Pzt Ring,Piezoelectric Ceramic Ring,Piezo Ceramic Ring
Zibo Yuhai Electronic Ceramic Co., Ltd. , https://www.yhpiezo.com